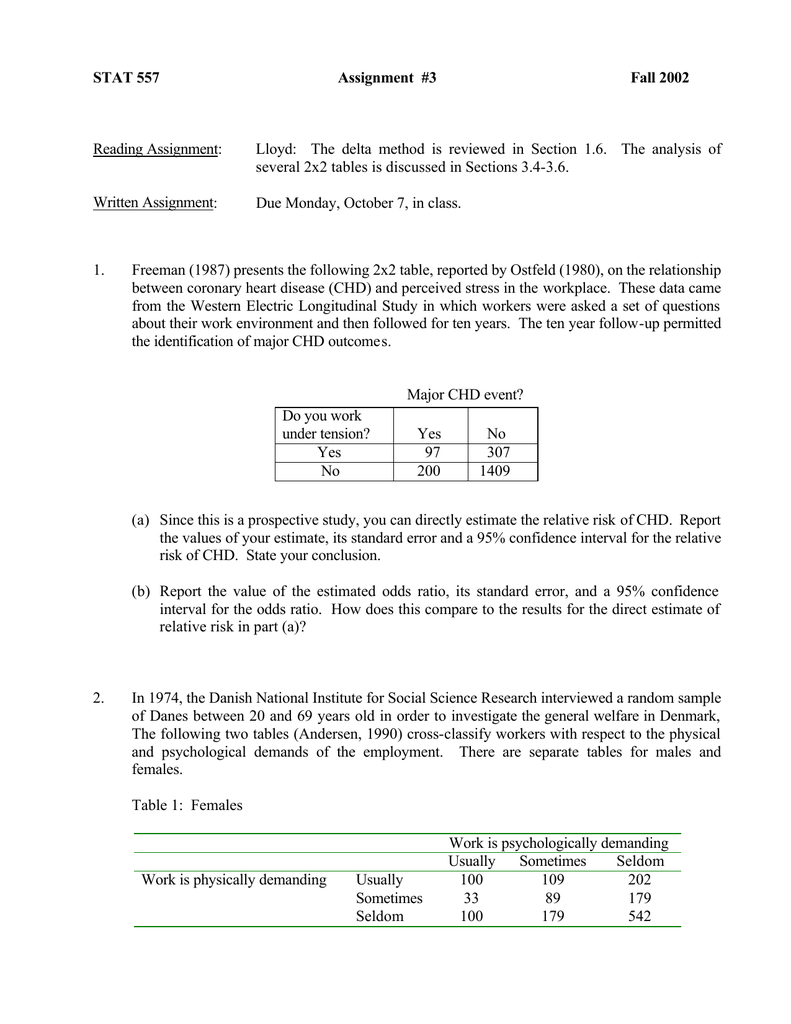
The basic difference is that the odds ratio is a ratio of two odds (yep, it's that obvious) whereas the relative risk is a ratio of two probabilities (The relative risk is also called the risk ratio) Let's look at an example Relative Risk/Risk Ratio Suppose you have a school that wants to test out a new tutoring programThe relative risk (RR) and the odds ratio (OR) are the two most widely used measures of association in epidemiology The direct computation of relative risks isRelative Risk, Odds, and Fisher's exact test I) Relative Risk A) Simply, relative risk is the ratio of p 1/p 2 For instance, suppose we wanted to take another look at our Seat belt safety data from Florida Safety equipment Injury in use Fatal Nonfatal Total None 1,601 165,527 167,128 Seat belt 510 412,368 412,878

Odds Ratio Relative Risk Calculation Definition Probability Odds Youtube
Odds ratio vs relative risk study
Odds ratio vs relative risk study- The odds ratio (OR) is the ratio of the odds of cancer in smokers to the odds of cancer in nonsmokers OR = (a/b)/ (c/d) = (ad)/ (bc) The risk ratio (RR), also called the relative risk, is the ratio of the probability of cancer in smokers to the probability of cancer in nonsmokers Given that you know a, b, c, and d, you can compute either ofOdds ratios (OR) are commonly reported in the medical literature as the measure of association between exposure and outcome However, it is relative risk that people more intuitively understand as a measure of association Relative risk can be directly determined in a cohort study by calculating a risk ratio (RR)



1 Calculate The Odds Ratio The 95 Confidence Chegg Com
An example of what I am talking about is the choice between risk ratio and odds ratio Odds ratio vs risk ratio You know the difference between risk and odds A risk is the proportion of subjects with an event in a total group of susceptible subjects Thus, we can calculate the risk of having a heart attack among smokers (infarcted smokersThe odds ratio and the relative risk will not always disagree by this much Large effects on groups with high initial risk seem to cause the most problems See Davies et al (1998) for some useful guidelines for when the odds ratio and relative risk are likely to differ When they do differ, the relative risk represents the typical interpretationWhen the disease is rare, the odds ratio will be a very good approximation of the relative risk The more common the disease, the larger is the gap between odds ratio and relative risk In our example above, p wine and p no_wine were 0009 and 0012 respectively, so the odds ratio was a good approximation of the relative risk OR = 0752 and RR = 075
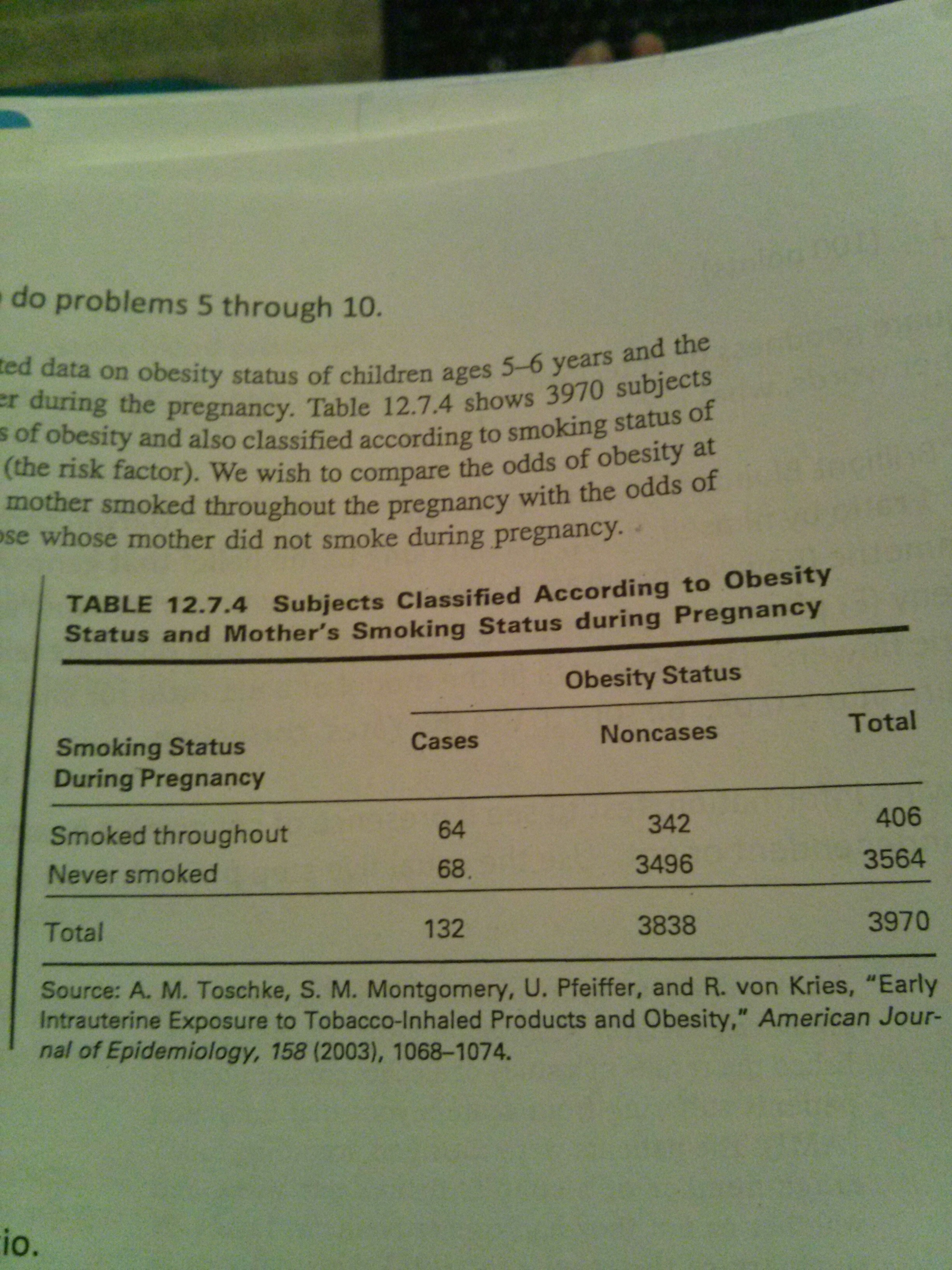
Subsequently, the term relative risk commonly refers to either the risk ratio or the odds ratio However, only under certain conditions does the odds ratio approximate the risk ratio Figure 1 shows that when the incidence of an outcome of interest in the study population is low (Relative risk is the ratio of the risks for an event for the exposure group to the risks for the nonexposure group Attack Rate (Risk) Attack rate for exposed = a ⁄ ab Attack rate for unexposed = c ⁄ cd For this example Risk of tuberculosis among East wing residents = 28 ⁄ 157 = 0178 = 178% Risk of tuberculosis among West wing residents = 4 ⁄ 137 = 0029 = 29% The risk ratio is simply the ratio of these two risks Risk ratio = 178 ⁄ 29 = 61
If the risk ratio is 1 (or close to 1), it suggests no difference or little difference in risk (incidence in each group is the same) A risk ratio > 1 suggests an increased risk of that outcome in the exposed group A risk ratio < 1 suggests a reduced risk in the exposed group Percent Relative Odds vs relative risk Odds vs relative riskWhen the risk ratio cannot be obtained directly (such as in a casecontrol study), the odds ratio is calculated and often interpreted as if it were the risk ratio Subsequently, the term relative risk commonly refers to either the risk ratio or the odds ratio However, only under certain conditions doesThe odds ratio ((a/c)/(b/d)) looks at the likelihood of an outcome in relation to a characteristic factor In epidemiological terms, the odds ratio is used as a point estimate of the relative risk in retrospective studies Odds ratio is the key statistic for most casecontrol studies




Abdullah Kharbosh What Does An Odds Ratio Or Relative Risk Mean By Ebmteacher Casecontrol Cohort T Co Shfiaepl57 عبر Slideshare



Ppt Odds Ratio Vs Relative Risk Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id
Both the odds ratio and the relative risk compare the relative likelihood of an event occurring between two groups The relative risk is easier to interpret and is consistent with general intuition Some designs, however, allow only for the calculation of the odds ration Covariate adjustment is easier for an odds ratio Even with initial risks as high as 50% and very large reductions in this risk (odds ratios of about 01), the odds ratio is only 50% smaller than the relative risk (01 for the odds ratio compared with a true value for the relative risk of 02) Odds ratio ended up appearing in Question 2 from the second Primary Exam paper of 08, and therefore a more extensive discussion of OR and risk is carried out in the CICM Primary statistics summaries Relative risk reduction RRR= absolute risk reduction divided by the control group risk




Comparing A Relative Risk To An Odds Ratio Just Data Things




Relative Risks Odds Ratios The Relative Risk Two Binomials Coursera
About Press Copyright Contact us Creators Advertise Developers Terms Privacy Policy & Safety How works Test new features Press Copyright Contact us CreatorsRelative Risk (RR) & Odds Ratio (OR) The difference between odds and probability is important because Relative Risk is calculated with probability and Odds Ratio is calculated with odds Relative Risk (RR) is a ratio of probabilities or put another way it is one probability divided by another Odds Ratio (OR) is a ratio or proportion of oddsRelative Risk Relative risk is a ratio of the risks of two groups In the example described above, it would be the risk of heart attack for a person in their current condition compared to the risk of heart attack if that person were in the normal ranges However, to truly interpret the severity of a relative risk we have to know the baseline risk




Relative Risk Analysis And Odds Ratio Analysis




Relative Risk Or Odds Ratio And 95 Confidence Intervals For Download Scientific Diagram
If odds are stated as an A to B chance of winning then the probability of winning is given as P W = A / (A B) while the probability of losing is given as P L = B / (A B) What does Relative Risk tell you?See all my videos at https//wwwzstatisticscom/videos/Health Stats IQ playlisthttps//youtubecom/playlist?list=PLTNMv857s9WUI5YsQMW14trmbopjZMWPa000 Int2) Relative Risk and Odds Ratio for the nonobese Relative Risk and Odds Ratio for the obese 3) Overall, you can see that decreasing the baseline incidence will decrease the odds ratio (300 in those who are nonobese versus 129 in those who are obese) Obviously, these results run counter



Arxiv Org Pdf 1510



Www Iapsmupuk Org Journal Index Php Ijch Article Download 1402 1044
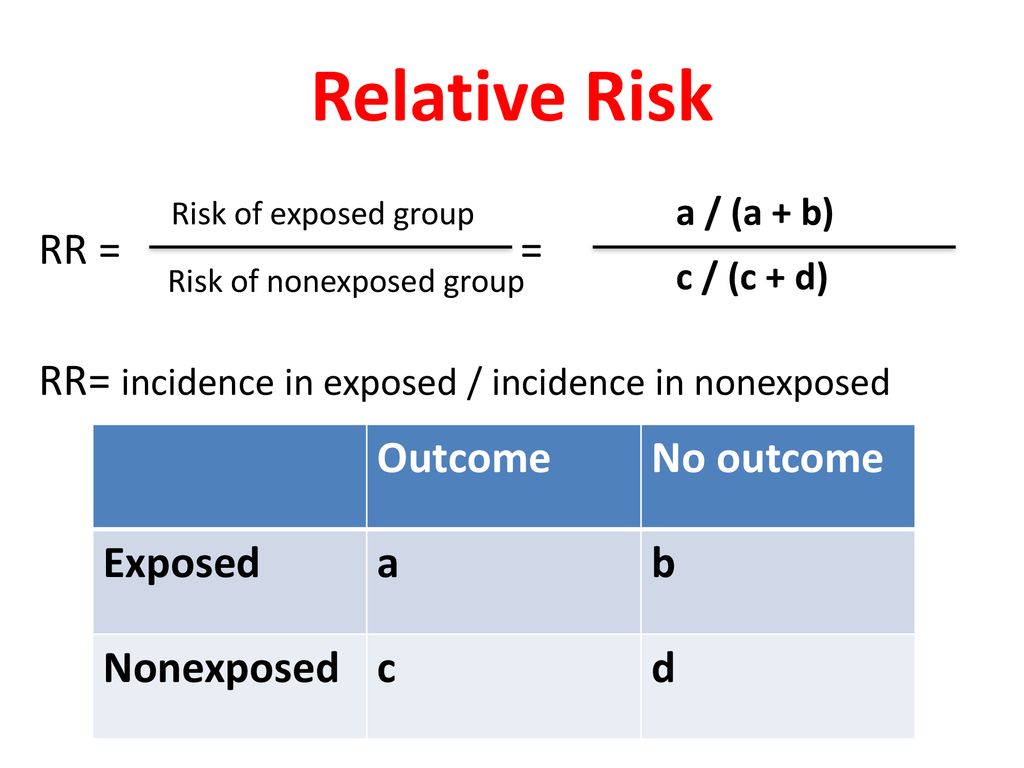
The odds ratio will be greater than the relative risk if the relative risk is greater than one and less than the relative risk otherwise In the example above, if the adjusted odds ratio were interpreted as a relative risk, it would suggest that the risk of antibiotic associated diarrhoea is reduced by 75% for the intervention relative to the placebo group Thus the odds ratio is (a/b) / (c/d) which simplifies to ad/bc This is compared to the relative risk which is (a / (ab)) / (c / (cd)) If the disease condition (event) is rare, then the odds ratio and relative risk may be comparable, but the odds ratio will overestimate the risk if the disease is more commonLet us now look at the relation between the relative risk and the odds ratio (Zhang and Yu, 1998) OR= ˇ 1 1 1ˇ 1 ˇ 2 1 ˇ 2 = ˇ ˇ 2 1 2 1 1 = RR 2 1 (21) From this we see that OR is always further away from 1 than RR But, more importantly, we see that the odds ratio is close to the relative risk if probabilities of the outcome are small (Davies et al, 1998)



Ae Incidence Screen



2
For estimates of odds ratios, this is logit (ie the logarithm of the odds of the mean); Odds ratio is similar to relative risk In the sheepskin trial the relative risk was 058 and the odds ratio was 054 For most clinical trials where the event rate is low, that is less than 10% of all participants have an event, the odds ratio and relative risk can be considered interchangeable For more than years, there has been debate about the relative merits of risk ratios compared with odds ratios as estimates of causal associations between an exposure (such as smoking or medication for high blood pressure) and a binary outcome (such as death vs life)




Critical Numbers Living With Risk Ppt Download




Odds Ratios And Relative Risks John Snow Cholera Data
For estimates of relative risk ratios, this becomes logarithm We can specify this manually, or just use a builtin family for our generalized linear model for which the logarithm is the canonical link fucntion, and hence the default Odds ratios and relative risks are interpreted in much the same way and if and are much less than and then the odds ratio will be almost the same as the relative risk In some sense the relative risk is a more intuitive measure of effect sizeThe risk ratio (or relative risk) is the ratio of the risk of an event in the two groups, whereas the odds ratio is the ratio of the odds of an event (see Box 92a) For both measures a value of 1 indicates that the estimated effects are the same for both interventions




Relative Risk Odds Ratios Youtube



Icare An R Package To Build Validate And Apply Absolute Risk Models
√1000以上 odds ratio vs relative risk usmle Odds ratio vs relative risk usmle The Relative Risk Ratio and Odds Ratio are both used to measure the medical effect of a treatment or variable to which people are exposed The effect could be beneficial (from a therapy) or harmful (from a hazard) Risk is the number of those having the outcome of interest (death, infection, illness, etc) divided by the total number exposed to Percent increase = (Risk Ratio lower bound – 1) x 100 Percent decrease = (1 – Risk Ratio upper bound) x 100 It's worth stating again when comparing two proportions close to 1 or 0, the risk ratio is usually a better summary than the raw difference Odds Ratios We now turn to odds ratios as yet another way to summarize a 2 x 2 table




1 Calculate The Odds Ratio The 95 Confidence Chegg Com



Http People Stat Sc Edu Hansont Stat5 Lecture19 Pdf
Risk is often a more intuitive concept than odds, and thus understanding relative risks is often preferred to understanding relative odds However, OR does not suffer from the same causal assumption limitations as RR, making it more widely applicable RELATIVE RISK AND ODDS RATIO Risk and Odds just seemed the same to me for a long time Since then, I have come to understand to important difference Lets start with Relative Risk Relative Risk can be addressed by asking the following question How many times more likely is an "exposed" group to develop aThe relative risk is best estimated using a population sample, but if the rare disease assumption holds, the odds ratio is a good approximation to the relative risk — the odds is p / (1 − p), so when p moves towards zero, 1 − p moves towards 1, meaning that the odds approaches the risk, and the odds ratio approaches the relative risk




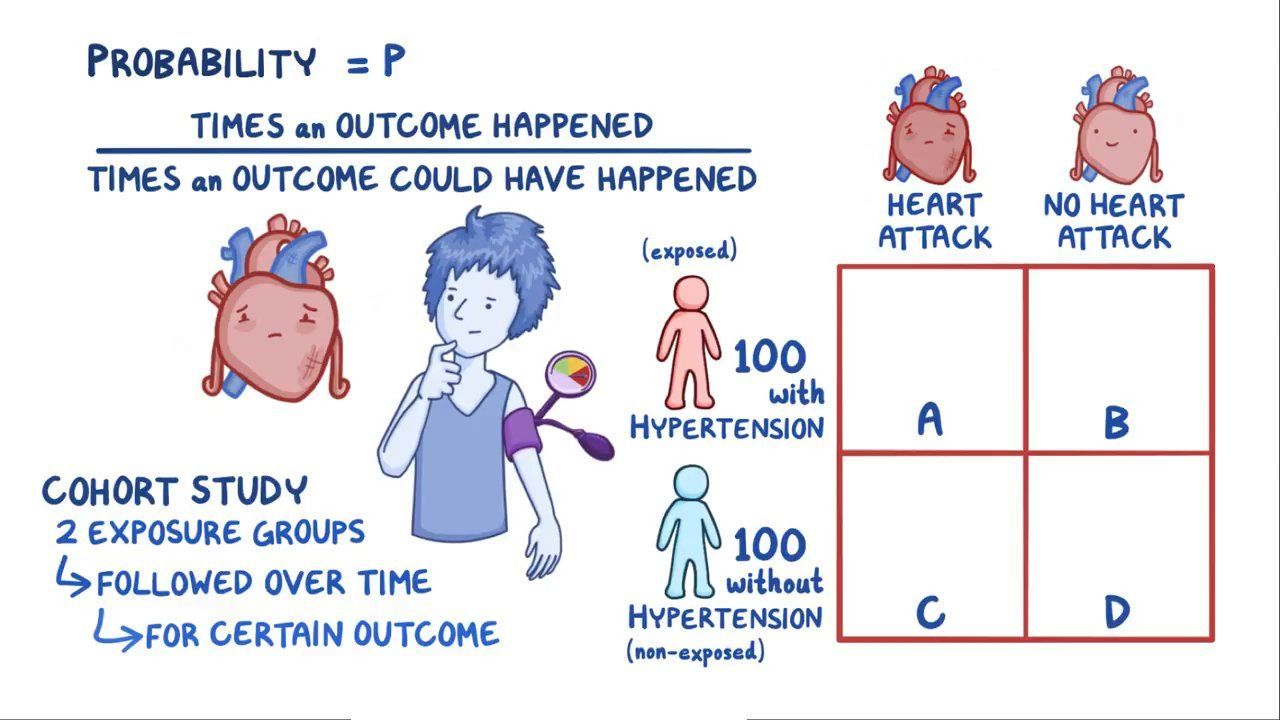
Analytical Studies Note Cohort Study Gives Incidence Relative Risk A R P A R Natural History Of Disease Cohort Study Case Control Study Study



Www Jstatsoft Org Index Php Jss Article View V086i09 V86i09 Pdf
When the RR is exactly 1, the risk is unchanged For example, a report may state 'The relative risk of blindness in people given drug T was 15' This shows that the drug increased the risk of blindness Another measure that is used is the odds ratio For practical purposes, assume that the odds ratio is the same as the relative riskFor instance, a relative risk of 70% corresponds to an odds ratio of 07/(107)=233 however, it is clearer to say to the layman that a certain risk factor "increases the probability of a disease by 70%" (relative risk) rather than that it "increases the probability of the disease by an oddsDifferenz zwischen Odds Ratio und Relatives Risiko Differenz zwischen 21 Odds Ratio vs Relatives Risiko Das relative Risiko (RR) ist einfach die Wahrscheinlichkeit oder Beziehung zweier Ereignisse Nehmen wir an, A ist Ereignis 1 und B ist Ereignis 2 Man kann das RR erhalten, indem man B von A oder A / B dividiert



Epidemiology Stepwards




Relative Risks Odds Ratios Relative Measures Two Binomials Coursera
Odds vs relative risk Odds vs relative riskAbsolute Risk Reduction is the decrease in risk provided by an exposure Is a clinically useful measure of the value of anIn both cases the relative risk was 5, but with entirely different levels of impact Please note this example is not meant to be interpreted that taking care of your health is notThe absolute risk is the probability of an event in a sample or population of interest The relative risk (RR) is the risk of the event in an experimental group relative to that in a control group The odds ratio (OR) is the odds of an event in an experimental group relative to that in a control groupThe relative risk and the odds ratio are measures of association between exposure status and disease outcome in a population Relative risk In epidemiology, relative risk (RR) can give us insights in how much more likely an exposed group is to develop a certain disease in comparison to a nonexposed group Once we know the exposure and disease status of a research population,




Ppt Categorical Variables Relative Risk Odds Ratios Powerpoint Presentation Id




Relative Risk Wikipedia
Odds ratio (OR) is a statistic commonly encountered in professional or scientific medical literature Most readers perceive it as relative risk (RR), although most of them do not know why that When the study design allows for the calculation of a relative risk, it is the preferred measure as it is far more interpretable than an odds ratio The odds ratio is extremely important, however, as it is the only measure of effect that can be computed in a casecontrol study design




How To Interpret And Use A Relative Risk And An Odds Ratio Youtube



Onlinelibrary Wiley Com Doi Pdf 10 1002 Sim



Q Tbn And9gcr Ttka12jaocnx Gn3ox9ci1ggq18vcw9359i6hq2cschyusam Usqp Cau



Academic Oup Com Ije Article Pdf 24 2 464 24 2 464 Pdf




Simple Way To Visualise Odds Ratios In R Stack Overflow



1



Http Www Thejuliagroup Com Documents Assignment 3 computing relative risk and odds ratios Pdf




How To Tell The Difference Between A Hazard Ratio Relative Risk And Odds Ratio



Www Jclinepi Com Article S05 4356 9 Pdf



Odds Ratio Video Explanation Osmosis




Pdf What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios Semantic Scholar
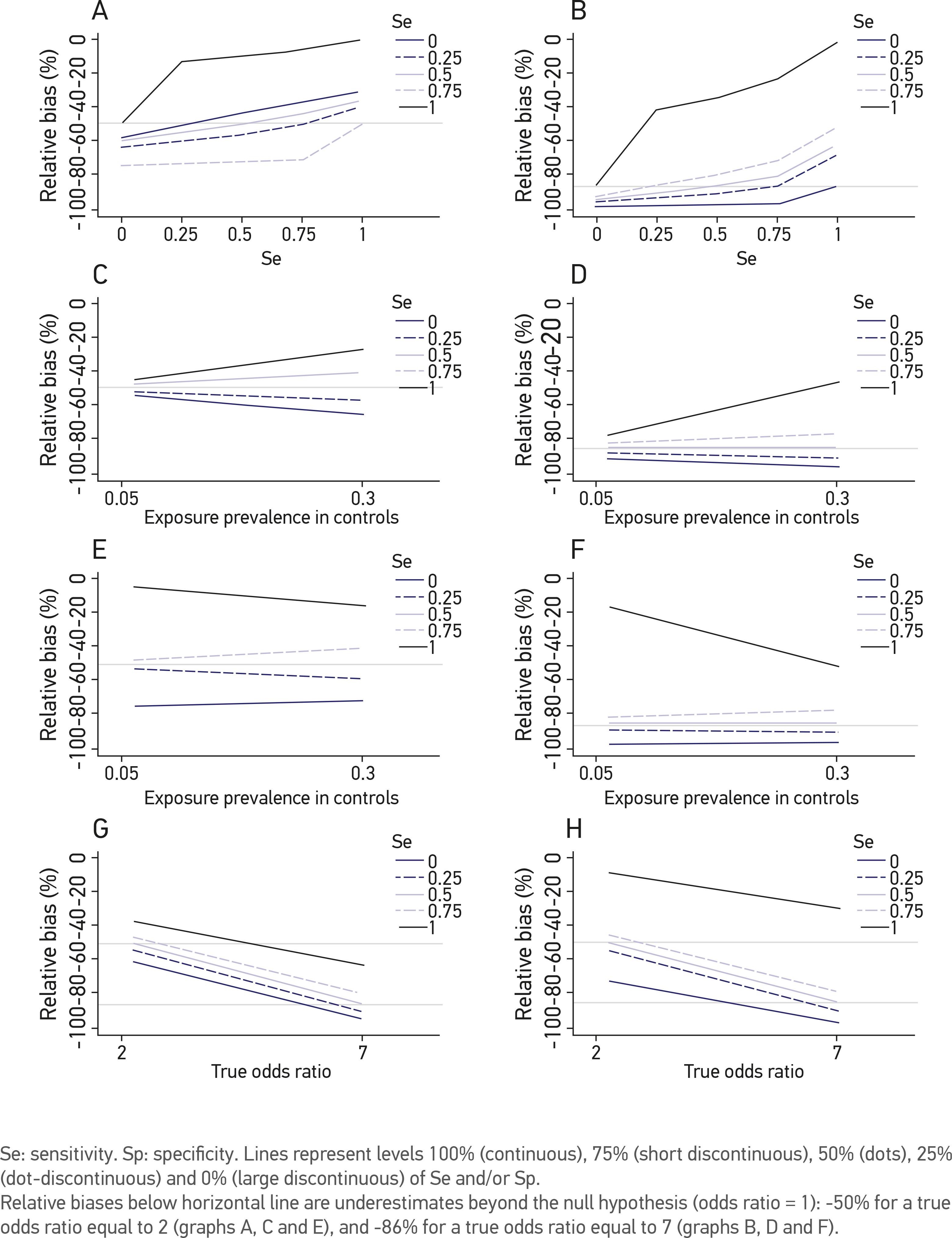



Scielo Brasil The Effect Of Misclassification Error On Risk Estimation In Case Control Studies The Effect Of Misclassification Error On Risk Estimation In Case Control Studies




Relative Risk 978 613 0 8




Comparing A Relative Risk To An Odds Ratio Just Data Things




Relative And Attributable Risks Epidemiology And Public Health Lecture Slides Docsity




A Simple Method For Estimating Relative Risk Using Logistic Regression Fredi Alexander Diaz Quijano Pdf Free Download



Arxiv Org Pdf 2105




Evidencebased Journal Club Intentiontotreat Odds And Risk Paul



Studying Studies Part I Relative Risk Vs Absolute Risk Peter Attia
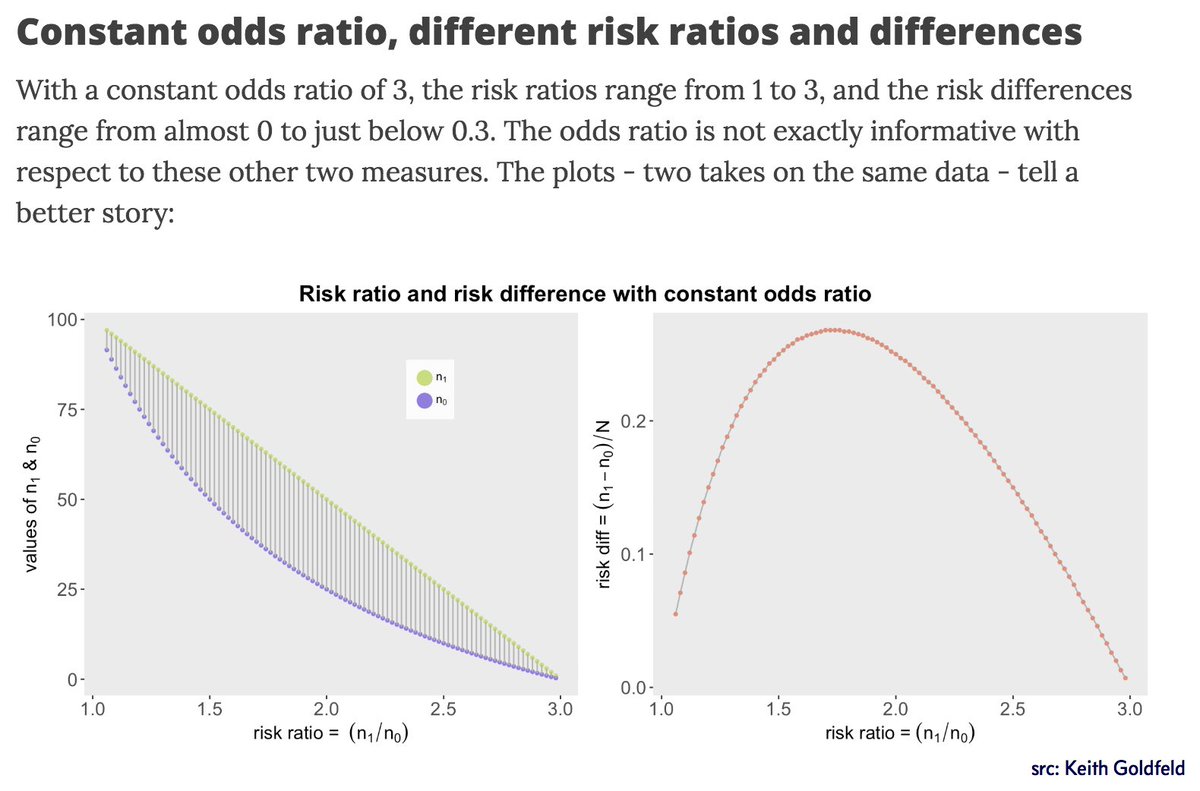



Mara Averick As Someone Who Asks For Odds Ratios And Relative Risk At The Vet I This Post How The Odds Ratio Confounds A Brief Study In A




Against All Odds Improving The Understanding Of Risk Reporting British Journal Of General Practice




What Is An Odds Ratio And How Do I Interpret It Critical Appraisal




Ppt Exploratory Data Analysis With Two Qualitative Variables Powerpoint Presentation Id




Statistc 111 Lecture Notes Spring 19 Lecture 11 Odds Ratio Relative Risk Ert2




Measures Of Effect Relative Risks Odds Ratios Risk Pdf Relative Risk Confidence Interval




Iv Estimate And Interpret The Relative Risk Chegg Com




Odds Ratio Relative Risk Risk Difference Statistics Tutorial 30 Marinstatslectures Youtube Study Skills Statistics Tutorial




Aquaculture Magazine February March 17 Volume 43 Number 1 By Aquaculture Magazine Issuu




Ppt The Odds Ratio Relative Odds Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 6056



Plos One Smoking And Suicide A Meta Analysis




Ci For Or And Rr Relative Risk Odds Ratio




Odds Ratio Relative Risk Calculation Definition Probability Odds Youtube




Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios




How To Calculate Odds Ratio And Relative Risk In Excel Statology




Risk Estimates Relative Risk Ratio And Odds Ratio Analyses For Download Table




Odds Ratio Relative Risk



Beaumont Cloud Cme Com Launchscorm Aspx Caseid 112 Userid 0 Video True




Relative And Attributable Risks Ppt Download




Pdf When To Use The Odds Ratio Or The Relative Risk




When Can Odds Ratios Mislead The Bmj




Relative Risk Versus Odds Ratio Usmle Biostatistics 4 Youtube



Forest Plots Of Relative Risks And Odds Ratios Of Detecting Fecal Download Scientific Diagram




Relative Risk And Odds Ratio R Erol Sezer Ppt Download




Effect Sizes Basicmedical Key



Q Tbn And9gcqsrft9mxr7dpz7nmjrd2rigdx Ivp6aahq2v9iti13quuix7yw Usqp Cau




Pdf Analysing Longitudinal Data On Students Decimal Understanding Using Relative Risk And Odds Ratios Semantic Scholar
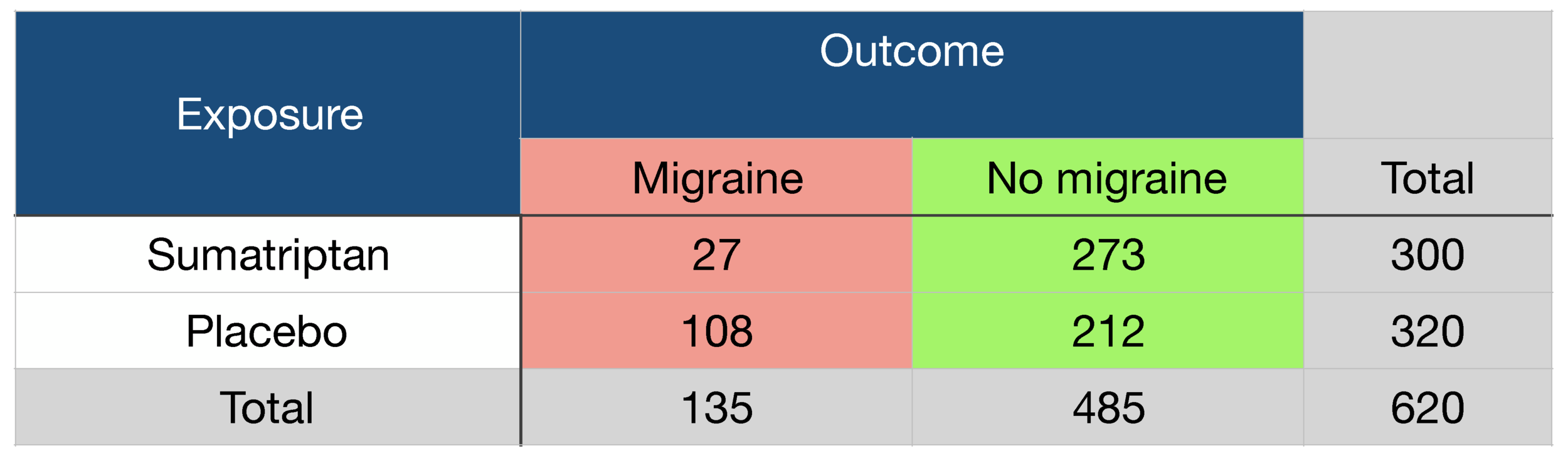



Probability Odds Ratio And Relative Risk Gp Raj



Http Www Floppybunny Org Robin Web Virtualclassroom Stats Basics Articles Odds Risks Proportions Odds Risks Sistrom 04l Pdf



Www Jstor Org Stable




Relative Risk Odds Ratio Attributable Risk And




Relative Risk Of Ocular Disease Secondary To Myopia A Downloadable Chart Ocular Risk Disease




Critical Numbers Living With Risk Ppt Download




Estimated Relative Risk Rr Compared With Odds Ratio Or For All Download Scientific Diagram




Relative Risk Odds Ratios Of Leptospira Infection Derived From An Download Table




Ppt Case Study Relative Risk And Odds Ratio Powerpoint Presentation Id



Www Jstor Org Stable



Video 01 Understanding Odds Ratios And Relative Risks The University Of Sheffield Kaltura Digital Media Hub
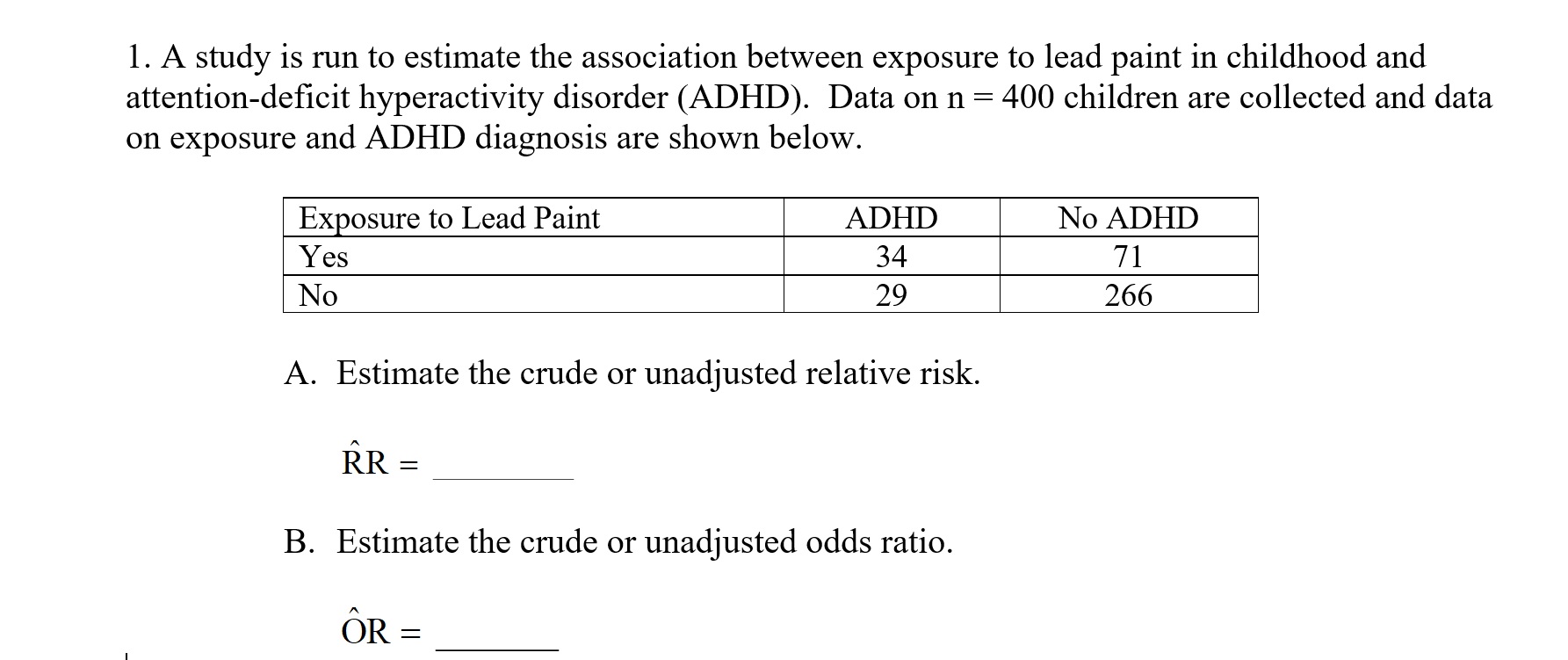



Answered 1 A Study Is Run To Estimate The Bartleby



Www Jclinepi Com Article S05 4356 10 9 Pdf




Ger1000 Chapter 4 More On Observational Studies Studocu




Understanding Systematic Reviews And Meta Analysis Archives Of Disease In Childhood




Comparing A Relative Risk To An Odds Ratio Just Data Things




Activity 4 Identification Of Risk Relative Risk Chegg Com



Document




Odds Ratios Vs Risk Ratios Stats By Slough



1




Odds Ratio Relative Risk Risk Difference Statistics Tutorial 30 Marinstatslectures Youtube




Converting An Odds Ratio To A Range Of Plausible Relative Risks For Better Communication Of Research Findings The Bmj




Using Odds Ratio In Case Control Studies Youtube




How To Tell The Difference Between A Hazard Ratio Relative Risk And Odds Ratio




Cramsurg Chapter 6 Odds Ratio And Relative Risk Youtube




Odds Ratios And Risk Ratios Youtube




Fully Adjusted Odds Ratio Or Relative Risk For Hypertension Compared Download Scientific Diagram



2




Odd Ratio Relative Risk And Attributable Risk Youtube




B Relative Risk And Odds Ratios Examples Relative Risk And Odds Ratios Examples Studocu



Absolute Risk Vs Relative Risk Vs Odds Ratio Pp Made Easy On Vimeo




Ppt The Odds Ratio Relative Odds Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 6056




What Is A Risk Ratio Epidemiology And Psychiatric Sciences Cambridge Core




Pdf Using Sas Procedures Freq Genmod Logistic And Phreg To Estimate Adjusted Relative Risks A Case Study Semantic Scholar



Effect Estimates And The Role Of The Chance Ppt Download




Cureus What S The Risk Differentiating Risk Ratios Odds Ratios And Hazard Ratios



0 件のコメント:
コメントを投稿